1. General Urology, Congenital Anomalies

used to be a branch of General Surgery, but several last decades a separate specialization, extensive diagnostics and conservative treatment, broad range of operative methods, broad range of operative methods
2. UTI, urolithiasis
2nd most frequentinfectionatall(1st –RTI), mostlyascending, normalurinarytractissterileupto distalurethra
predisposingfactors, pathogenes–Gram negative bacteria–in 90 %,...
3. Urooncology, retroperitoneum
incidence C60 in CZ 2004 1,1/ 100 000 men/y, rarein circumcisedatbirth(Jewsandotherreligiousgroups), Precancerosis, Carcinomain situ
4. Dysfunction of lower urinary tract
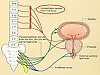
Bladder and urethra –a functional unit for storage and periodic expulsion of urine (micturition), storage and micturition are coordinated by different parts of CNS –functional disorders at every level cause neuropathic bladder, neuropathic bladder is a term apllied to voiding problems due to neurologic dysfunction of urinary bladder
5. BPH, prostatitis, benign diseases of genitals
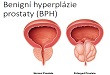
Non -malignant enlargement of prostate. Etiology unknown, a lot of theories may be related to an imbalance between estrogenic and androgenic activity. Histopathology. BPH – histhological diagnosis, patient comes because of voiding problems – LUTS (lower urinary tract symptoms).
6. Andrology, genitourinary trauma, urological emergency
mainly mycotic - diabetics –combination with diabetic phimosis –healthy men –intercourse with woman with mycotic vaginitis –Treatment, local antimycotics (Clotrimazolum), in phimosis -circumcision
Urology for medical students
UROLOGICAL SYMPTOMS
Frequency - normal adult voids five or six times per day, with a volume approximately 300ml with each void, often voiding = polakisuria (lat.)
Nocturia - frequent passage of urine during the night (nocturnal frequency)
Urgency - an overwhelming desire to pass urine immediately
Urge incontinence - wetting when voiding cannot be instituted quickly enough
Dysuria - pain on voiding, that is usually caused by inflammation
Urology for students of stomatology
Questions
1. Urinary tract infections, urolithiasis
2. Lower urinary tract dysfunctions (BPH - benign prostatic hyperplasia, neuropathic urinary bladder, urinary incontinence)
3. Urooncology – tumors of kidney, urinary bladder, prostate and testicle
4. Benign diseases of male genitalia, the most important urogenital anomalies, andrology
5. Operative approaches in urology, urological emergency